Detailed description of eMMC technology
Guide: eMMC is an embedded memory standard specification for products such as mobile phones or tablets. Now, mainstream flagship mobile phones use eMMC 5.0 flash or updated UFS 2.0 flash which has better reading performance than eMMC 5.0.
eMMC= NAND Flash + Flash Control Chip + standard Interface
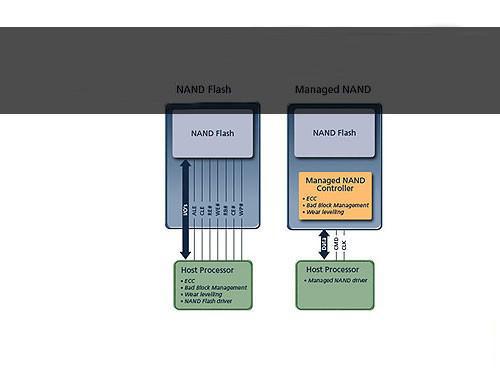
eMMC (Embedded Multi Media Card), established by the MMC Association, is an embedded memory standard specification primarily for products such as mobile phones or tablets. One obvious advantage of eMMC is the integration of a controller in the package that provides a standard interface and manages flash memory, allowing handset manufacturers to focus on other parts of product development and shorten the time to market products. These features are equally important for NAND vendors who want to reduce lithography size and cost.
Now, when the mainstream flagship mobile phones are using EMMC 5.0 flash, a new flash specification quietly emerge. It is UFS 2.0 flash standard that has better reading performance than eMMC 5.0.
Here's how eMMC accelerates speed?
Reading speed of mobile phone micro-disk is up to 50 MB/s
Before starting today's topic, please go back with the author, and recall the 2011 annual multimedia mobile phone cross-evaluation. The result of cross-evaluation is not the focus. Whether you have noticed or not, one of the running scores of ANTUTU, known as SD card reading speed, is worth deep study. Each review will always be doubted by netizens that why SD card reading and writing speed among all products evaluated is 0. Here the author will give a unified answer to this question once again: ANTUTU’s running scores tool requires tested products with more than more than 300MB of built-in storage space, that is, the product under test without inserting any external SD card, should ensure that there is more than 300MB of read-write built-in storage space.
Among 16 products involved in the cross-evaluation, 3 products have outstanding "SD reading speed" , Samsung Galaxy SⅡ (I9100), Meizu MX (dual-core version), and Xiaomi, respectively. Their test results are shown as ">50MB/s", which is basically twice than other products. why is that? This is today's theme: mobile phone micro-disk -- eMMC technology.
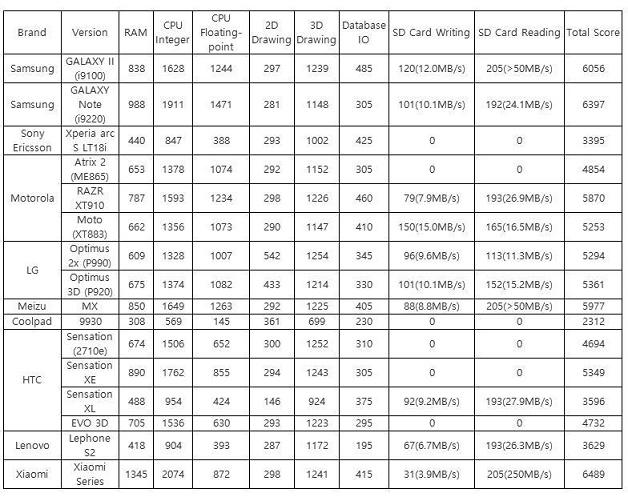
eMMC solution was used in only 3 products in the 2011 multimedia mobile phone cross-evaluation
Specially: ANTUTU Benchmark is a software dedicated to Android mobile phones and tablets. It can not only run a full test project with one click, like memory performance, CPU integer performance, CPU floating-point performance, 2D/3D drawing performance, database I/O, SD card read-write speed, and so on, scoring the overall and individual hardware performance of the phones, but also upload scores and view the device's ranking in the world.
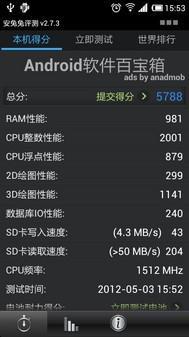
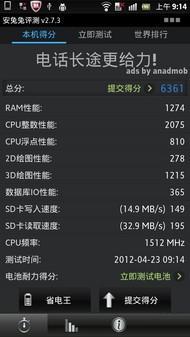
Mobile Phone with eMMC solution (left) "SD reading speed" is up to 50MB/s
Among them, RAM represents the throughput ability of the machine for data operations; CPU integer/floating-point performance represents the processor's computing ability; 2D/3D drawing performance represents the graphics processing chip's ability to render images, database I/O performance represents processor and RAM access efficiency to the database, SD card writing/reading speed indicates the read-write capability of the fuselage ROM (currently the test requires more than 300MB of ROM free space, so if the fuselage storage space/ROM is less than 300MB, the score will be ignored, but the total score is deducted from the corresponding score). Theoretically, the higher the score, the stronger the performance.
First of all, it is clear that built-in storage space and external memory card of mobile phone is two different concepts. Mobile memory cards mainly include TF card (Trans Flash, also known as microSD card), RS-MMC card (also known as mobile MMC card), and MMC card (multimedia card). The memory stick used by Sony Ericsson in the early days has pulled out of the history stage, while CF cards, SD cards, and miniSD cards are still a little far away from mobile phones.
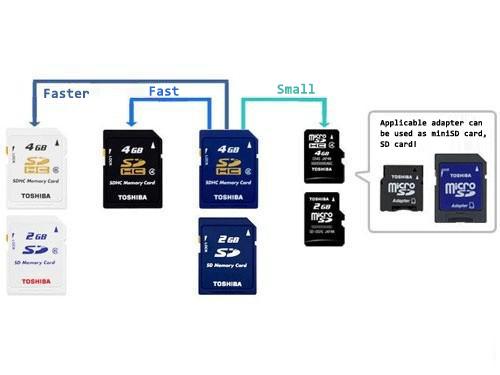
A variety of microSD memory cards commonly used in mobile phones
Different brands of mobile phone manufacturers have different technologies and hardware facilities, for example different sizes and specifications of memory card slot. As a result, the manufacturers have produced mobile phone memory cards of different sizes to match the use of different sizes of memory card slots and named them. The ultimate goal is simply to distinguish different sizes of memory cards by different names. We can generally think that different names of memory cards are actually different sizes.
Today's mobile phones, no longer just rely on external memory cards to expand their capacity, because phones themselves have built-in storage space up to 64GB. Thus, different storage space results in different speed of SD card reading speed just mentioned.

eMMC schemes of different brands are also different in size.
eMMC (Embeded Multimedia card) is not a new-size memory card, but an embedded memory standard specification set by the MMC Association, specifically designed for mobile phones and mobile embedded products. eMMC is simply an embedded storage solution that integrates a controller and provides a unified standard interface, in addition to conventional memory.
Design concept of eMMC is to simplify the use of mobile phone memory. Thanks to the integration of NAND flash chip and control chip into 1 MCP chips, mobile phone customers only need to purchase eMMC chip, rather than deal with other tedious NAND flash compatibility and management issues. The biggest advantage of eMMC is to shorten the marketing cycle, reduce R&D costs of new products and accelerate the speed of product innovation. Seeing here, there must be a part of people having understood what eMMC is. if still don’t understand, but want to make it clear, please continue to read the vernacular explanation on the last page.
Vernacular explanation of eMMC
In fact, eMMC adds an additional control chip on the basis of original built-in memory, and finally is encapsulated in a unified way with a standard interface for mobile phone customers to use directly. This is somewhat similar to MediaTek's MTK, or Qualcomm's Snapdragon solution. Mobile terminal manufacturers buy not only a CPU, but a complete set of solutions. As a result, the operation is simplified and compatibility between different brand of hardware is avoided. The above 3 products can stand out in SD card reading speed, relying on eMMC. Of course, the use of eMMC built-in storage is more than these three. Left a deep impression on the author, the first Android4.0 dual-core smartphone-ZTE U970 also belongs to eMMC products.
With the increase of built-in storage reading speed in mobile phone, the direct benefit is improving execution efficiency, whether playing music videos, browsing the web, or playing games that consume most hardware resources. The so-called ROM reading speed is also an important indicator in addition to processor and RAM.
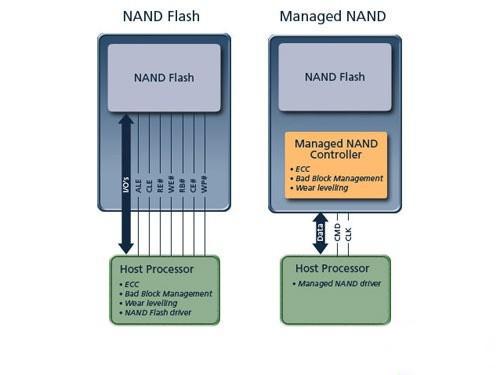
Comparison between NAND Flash (left) and eMMC (right)
Board members of the MMC Association include: ATP, ASUS, Gemplus, HP, Infineon, Intel, Itri, Kingston, Lexar, Micron, Nokia, Power Digital Card, Samsung Electronics, and Silicon Motion. After the latest eMMC4.5, eMMC new specifications will be led by Samsung Electronics UFS (Universal Flash Storage), which will even package the RAM in the future. Samsung has few adversaries in this regard.
eMMC= NAND Flash + Flash Control Chip + standard Interface
It is suggested that when you pay attention to our evaluation articles in the future, please focus on the score of "SD card reading speed" in ANTUTU running score, because this score is also closely related to the speed of application loading of the mobile phone.
