Introduction to the basic concept and classification of memory (1)
Guide: All information in the computer, including input raw data, computer programs, intermediate running results and final running results are stored in memory.
Introduction to the basic concept and classification of Memory
What is memory?
Memory is a memory device in a computer system that stores programs and data. All information in the computer, including input raw data, computer programs, intermediate running results and final running results are stored in memory. It stores and retrieves information based on the location specified by the controller.
Composition of Memory
Semiconductor devices and magnetic materials are the main storage medium for memory. The smallest storage unit in memory is a bi-stable semiconductor circuit or a CMOS transistor or a magnetic material storage unit that can store a binary code. A storage unit is composed of several storage elements, and then many storage units are made up of a memory. A memory contains many storage units, each of which can store one byte. The location of each storage unit has a number, that is, the address, which is generally expressed in hexadecimal system. The sum of data that can be stored by all storage units in a memory is called its storage capacity. Assuming that the address code of a memory consists of 20 bits of binary digits (that is, 5 bits of hexadecimal digits), it can represent 220, that is, the address of 1M storage units. Each storage unit stores one byte, and the storage capacity of the memory is 1KB.
Classification of memory
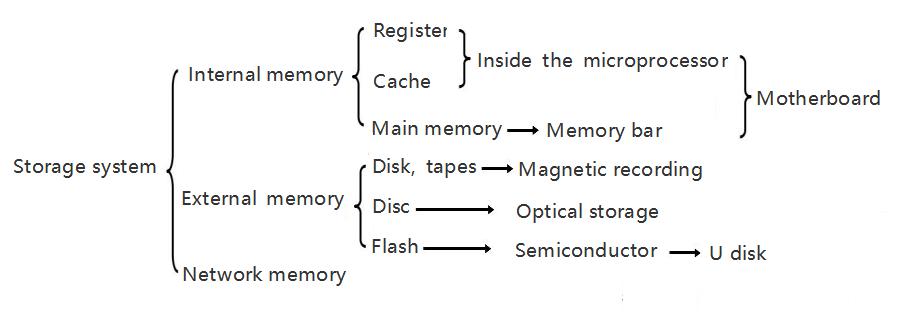
1. Sort by storage medium
(1) Semiconductor memory: a memory consisting of semiconductor devices. U disk is a semiconductor memory which is integrated by flash chips, and its storage medium is semiconductors.
(2) Magnetic surface memory: a memory made of magnetic materials.
2. Sort by storage mode
(1) Random memory: The contents of any storage unit can be accessed randomly, and access time is independent of physical location of the storage unit.
(2) Sequential memory: It can only be accessed in a certain order. The access time is related to physical location of the storage unit.
3. Sort by read-write function of memory
(1) Read-only memory (ROM): A semiconductor memory whose stored content is fixed and can only be read out but not written.
(2) Random read-write memory (RAM): A semiconductor memory that can be read and written.
4. Sort by the preservability of information
(1) Non-permanent memory: A memory that loses information after power failure.
(2) Permanent memory: A memory that can still store information after power failure.
5. Sort by the function in computer system
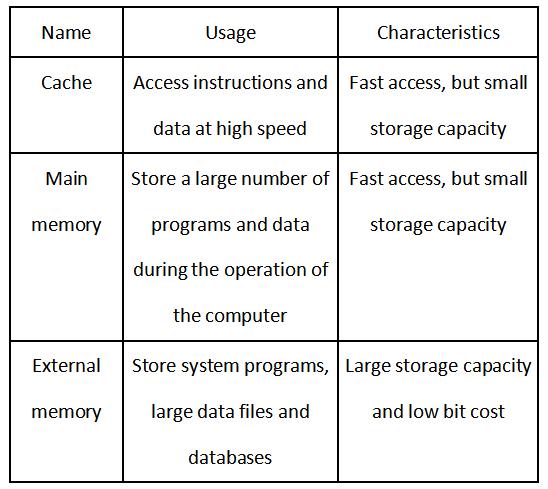
According to the function of memory in computer system, it can be divided into main memory, auxiliary memory, cache, control memory and so on.
In order to solve the contradiction among large capacity, fast speed and low cost, current memory usually adopts multi-level memory architecture, namely, the use of cache, main memory and external memory.