SSD technology literacy: What is NVMe? What are the characteristics of NVMe SSD?
Guide: NVMe SSD refers to the SSD with NVMe standard. Both NVMe and AHCI are actually the interface standard of logical devices, not the interface! The NVMe standard is for PCI-E SSD.
Those who have installed and configured SSD by themselves should know that if they want SSD to play its real performance, they will enter BIOS and switch SATA controller mode to AHCI. For SATA devices, using AHCI mode is indeed the right choice to achieve better performance. But now the latest storage interfaces such as M.2 and SATA-E are all PCI-E channels. AHCI is not a good choice for PCI-E, because PCI-E using a new NVMe standard can play the best performance.
What is NVMe?
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is a standard (or protocol) based on M.2 interface, which is specially designed for flash memory. It's not an interface.
Similar standards (or protocols) include AHCI, etc.
NVMe SSD Products
SAMSUNG 960 EVO 250G M.2 NVMe Solid State Drive
Intel 600P Series 128G M.2 2280 Interface Solid State Drive and so on are all based on NVMe standard. When purchasing SSD, we usually see the specification parameters marked by the manufacturer as follows:
Interface: M.2 Interface (NVMe Protocol)
Driven by Intel and Samsung, products originally only used in enterprise-class products have entered client-class market. As the interface of high-end SSD has been shifted to PCI-E and M.2, the old AHCI standard is out of date. When more and more master control manufacturers have introduced the master control with NVMe, there will be more SSDs with NVMe standards introduced to the market in the future. However, what is NVMe?

A number of people may know a lot about AHCI, but actually both NVMe and AHCI are interface standard of logical device rather than interface. NVMe, short for Non-Volatile Memory Express, is a specification for SSD with PCI-E channel. NVMe has primarily made full use of the low latency and parallelism of PCI-E SSD, as well as parallelism among processor, platform and application. Both hardware and software in host can utilize fully parallelism of SSD. Compared with the current AHCI standard, NVMe standard can bring various performance improvements.
Origin of NVMe standard (also known as protocol)
The SATA interface and AHCI standard used today are actually designed for high-latency mechanical hard drives. At present, mainstream SSDs continue to use SATA interface and AHCI standard. Early SSDs may not be found any problems when their performance is not high. However, with the increasing performance of SSDs, these standards have become a major bottleneck restricting SSDs. AHCI standard designed for mechanical hard drives is not very suitable for low-latency SSDs.
Of course, the industry has long been aware of this problem. In the second half of 2009, the technical work on NVMe was officially launched. The NVMe specification was customized by a working group of more than 90 companies, among which Intel was the main leader and members included Micron, Dell, Samsung, Marvell, NetAPP, EMC, IDT and so on. The purpose was to establish new storage specification standards for SSDs, freeing them from old SATA and AHCI.
In 2011, NVMe standard customized according to the characteristics of flash memory was officially released. This new standard relieved the restrictions of SSD imposed by old standards. The standard was upgraded to NVMe 1.1 in 2012, and the latest NVMe 1.2 standard was launched in 2014.
The first product supporting NVMe standard was Samsung XS1715, which was released in July 2013, followed by an enterprise-class SSD with NVMe standard. NVMe standard products begin to enter client-class market until the release of Intel 750 this year.
Advantages of NVMe SSD
First advantage of NVMe SSD is low latency.
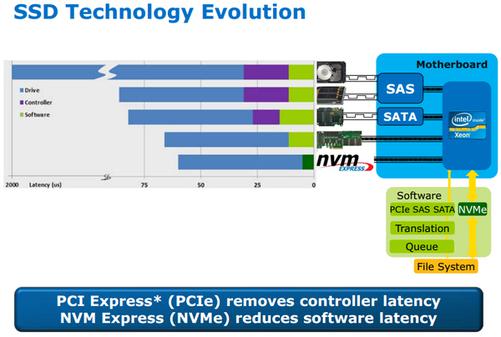
When it comes to the advantages of NVMe standard compared with AHCI standard, one of them is low latency. Please look at intuitive image above. NVMe standard is oriented to PCI-E SSD. Direct connection between native PCI-E channel and CPU eliminates the delay caused by communications between external controller (PCH) of SATA and SAS interface and CPU.
In terms of software, the latency of NVMe standard is less than half of that of AHCI because NVMe simplifies the invocation and does not need to read registers when executing commands. However, AHCI requires reading registers four times for each command, which consumes 8000 CPU cycles, resulting in a delay of about 2.5 microseconds.
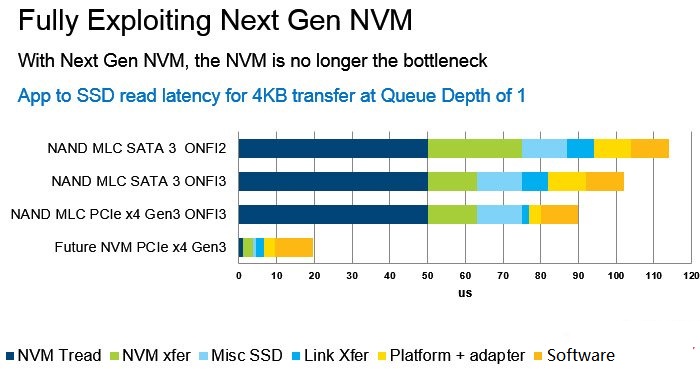
Lower latency can boost SSD performance for 4KB transfer at QD1.
Second advantage of NVMe SSD is IOPS improvement.
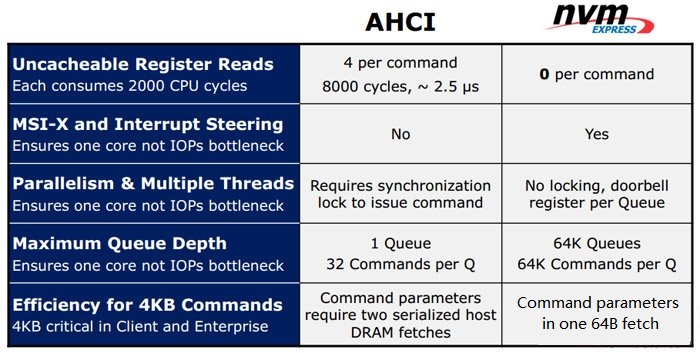
In addition, NVMe also greatly improves the IOPS performance of SSD. The idea of parallelism is not fully integrated into AHCI specification. NCQ function can be used to optimize the transmission capability, but the interface does not allow SSD to really maximize its parallelism.
Now SSD testing usually tests the IOPS capability at queue depth of 32 at most which is actually the upper limit of AHCI. Many flash master controls can provide better queue depth. NVMe increases the maximum queue depth from 32 to 64000 so that the IOPS capability of SSD will be greatly improved.
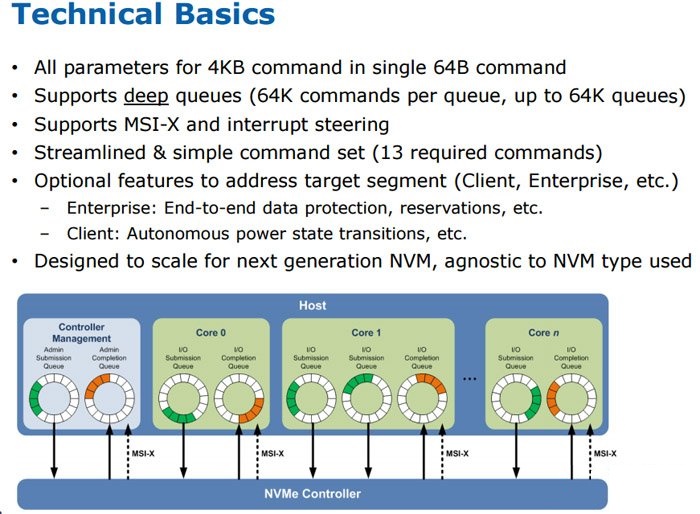
NVMe also supports accepting commands and prioritizing requests from multi-core processors at the same time, a feature that becomes apparent at enterprise-class heavy load.
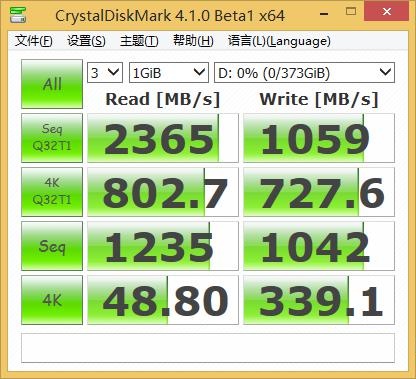
The advantage of low latency and good parallelism is that the randomness of SSD can be greatly improved. The Intel 750 we have tested is a NVMe SSD whose randomness is absolutely first-class, and it can play an excellent speed at any queue depth.
Third advantage of NVMe SSD is lower power consumption.
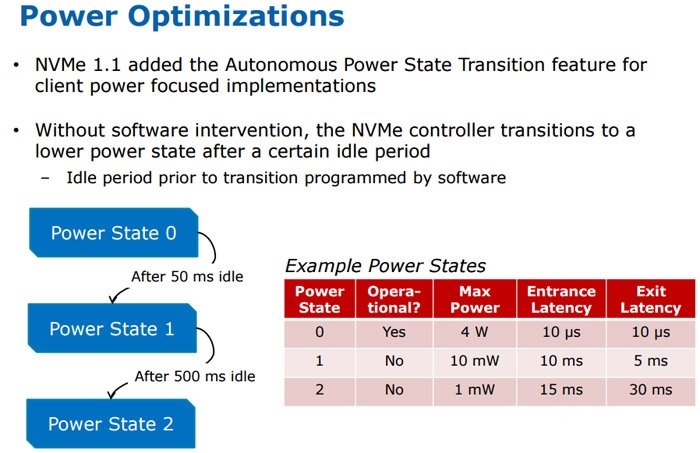
NVMe adds the feature of automatic power state transition and dynamic energy management. The device can transit from Power State 0 to Power State 1 after 50ms idle. If it continues to be idled, it will enter Power State 2 with lower power consumption after 500ms. There will be a short delay in switching. The NVMe SSD can be controlled at a very low power consumption for a short time when being idled, a significant advantage compared with current mainstream AHCI SSD. In addition, this is especially important for mobile devices, which can significantly increase the endurance of notebooks and tablets.
Fourth advantage of NVMe SSD is wide applicability of drivers.

Driver compatibility is also a common problem for all PCI-E SSDs. Each PCI-E SSD has a dedicated driver for different systems. Some manufacturers do very well in this respect, while others do not. However, many PCI-E SSDs require loading drivers to boot normally.
The emergence of NVMe standard solves this problem. NVMe SSD can easily match different platforms and systems, and can work normally without the corresponding driver provided by the manufacturer. At present, NVMe SSD has supported Windows, Linux, Solaris, Unix, VMware, UEFI and so on. Of course, Intel products have their own drivers, and Intel SSD can work properly without installing its own drivers. However, its performance cannot be fully played, for example, Intel 750 tested previously exits this issue. It’s unclear whether other manufacturers have the same problem or not.
Related Articles:
As 100 thousand wafers being scrapped 7nm technology will be a main force of TSMC’s revenue in 2019
2018 profits of memory manufactuers double while their days have passed this year with a half investment
Write amplification is a critical parameter of SSD
