Recently, Samsung, Toshiba/Western Digital, Intel/Micro, SK Hynix, and Yangtze Memory(YMTC)have released their innovative technologies and strategic plans. Summarizing the technological development of original factories, the target of the second half of 2018 is to enter the stage of mass production of 64-layer QLC NAND and 96-layer TLC NAND. In 2019, the aim is to promote the development of 96-layer QLC NAND technology, making the capacity of single 3D NAND more than 1Tb.
With the rapid development of 3D NAND technology, it can be predicted that QLC will replace TLC, just as TLC replaces MLC. The single Die capacity of 3D NAND single continuous doubles, which will upgrade consumer-grade SSD to 4TB, enterprise SSD to 8TB, QLC SSD will carry the banner of replacing HDD.
Samsung started mass production of 96-layer 3D NAND and 64-tier QLC SATA SSD.
As a leader in the NAND Flash market, Samsung began to invest in 3D NAND as early as 2013. In 2018, Samsung began mass production of the fifth generation of 96-layer V-NAND. Compared with the previous generation of 64-layer V-NAND, its productivity can be increased by more than 30%. Samsung is currently launching 256Gb V-NAND on the 96-tier basis, and the data storage speed increases by 40% to 1.4Gbps. Later, it will launch a V-NAND with a capacity of up to 1Tb based on QLC architecture.
In addition, Samsung has mass production of SATA SSD based on the QLC, and V-NAND based on 64-layer single Die 1Tb QLC (4-bit-based). This new QLC SSD carries 32 chips with the maximum capacity of 4TB and the same technological performance as TLC SATA SSD, and provides 540MB/s reading speed and 520MB/s writing speed. What’s more, it has a three years warranty.

Toshiba / Western Digital can produce 96-layer 3D TLC NAND with volume production, and QLC will achieve mass production in early 2019.
In 2017, TOSHIBA and Western Digital announced that the technologies of 96-tier and QLC had been successfully worked out. In the first half of 2018, they increased the investment of equipment for Fab6 factory, and will construct a new Fab7 factory. In the second half of 2018, the news was announced that they had mass production of 96-tier 3D TLC NAND and successfully developed 96-tier QLC (4-bit) NAND.
96-Layer 3D TLC NAND of Toshiba will expand the quantity of products in Q4. It will also introduce new XG6 series SSD with a capacity from 256GB to 1TB. It will also propose 3D NAND with low latency, which is based on XL-Flash and similar to SLC NAND. Western Digital said that the 96-layer QLC (4-bit) NAND was successfully developed, with a single Die capacity of up to 1.33 Tb, and it is in the sample delivery stage, and it will be firstly used in consumer-grade flash products under the SanDisk brand, which will be sold in batches in the second half of the year.

Micron technology and Intel released 3D QLC NAND, which uses the technology of QLC to produce.
Micron technology and Intel began to produce 64-tier QLC (4-bit) NAND, whose capacity of a single Die is 1 Tb. Micron launched SSD of 5210 ION series, which was based on 64-tier QLC NAND, and has begun to supply goods to customers of its strategic partners. It is predicted that Micron will expand the supply in Q4. Intel launched PCIe SSD D5-P4320 in data center area, which is also based on 64-tier QLC and having the maximum capacity of 8TB. For the consumer-grade market, Intel launched QLC NAND 660P series SSD, with the maximum capacity of 2TB.

The second generation of 3D Xpoint, jointly developed by Micron and Intel, will enter the market in the first half of 2019. The sample of the next generation of 96-layer 3D NAND has been sent to customers and is expected to be produced in batches by the end of 2018.
SK Hynix launches 4D NAND with 96-layer stacked and 512Gb TLC
4D NAND of SK Hynix uses CTF (Charge Trap Flash) with smaller memory area, faster speed and more durability (more P/E times). Compared with the traditional architecture, the peripheral circuit (PUC, Peri. Circuits) architecture of 4D NAND can reduce the chip area, shorten processing time and reduce costs. Compared with 72-layer stacked V4 3D TLC, the area of 96-layer stacked 4D NAND stacked is reduced by 30%, the reading speed is increased by 25%, and the writing speed is increased by 30%.

The Yangtze Memory announced the new technology Xtacking, which will be used in the 64-tier 3D NAND and put into production in 2019.
Yangtze Memory (YMTC) announced its breakthrough technology, Xtacking, which brings 3D NAND high I/O performance, higher storage density, and shorter listing cycle, won the "the most innovative flash business" award in FMS Summit of the United States.
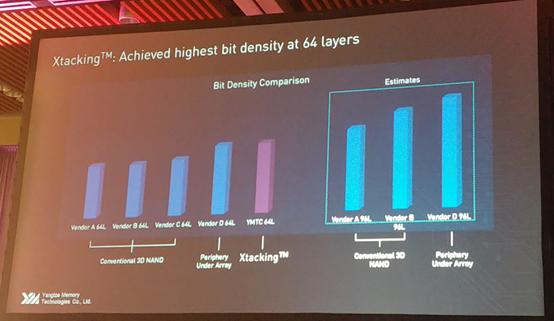
The Xtacking technology of Yangtze Memory shortens the product development time by three months, shortens the production cycle by 20%, and greatly increases the NAND I / O speed to 3.0 Gbps. It puts the peripheral circuit above the storage unit and has a higher storage density than the traditional 3D NAND. Yangtze Memory has already produced 32-layer 3D NAND in Wuhan Storage Base. The new technology called Xtacking will be applied to the development of the second generation of 64-layer 3D NAND products. It is planned to achieve mass production in 2019.